Puzzle Dungeon Sokoban Solver CLI - sokodun
Overview
sokodun is the command-line interface for the Puzzle Dungeon Sokoban Solver. It uses the
same solver code as the GUI and reports progress incrementally by
default.
Using a dedicated command-line tool improves performance and enables automation when solving entire collections.
Pressing Ctrl-C stops the current level solution (similarly to reaching a time limit). The user is then prompted either to continue with the next level by pressing Enter, or to terminate solving completely by pressing Ctrl-C again.
Basic Usage
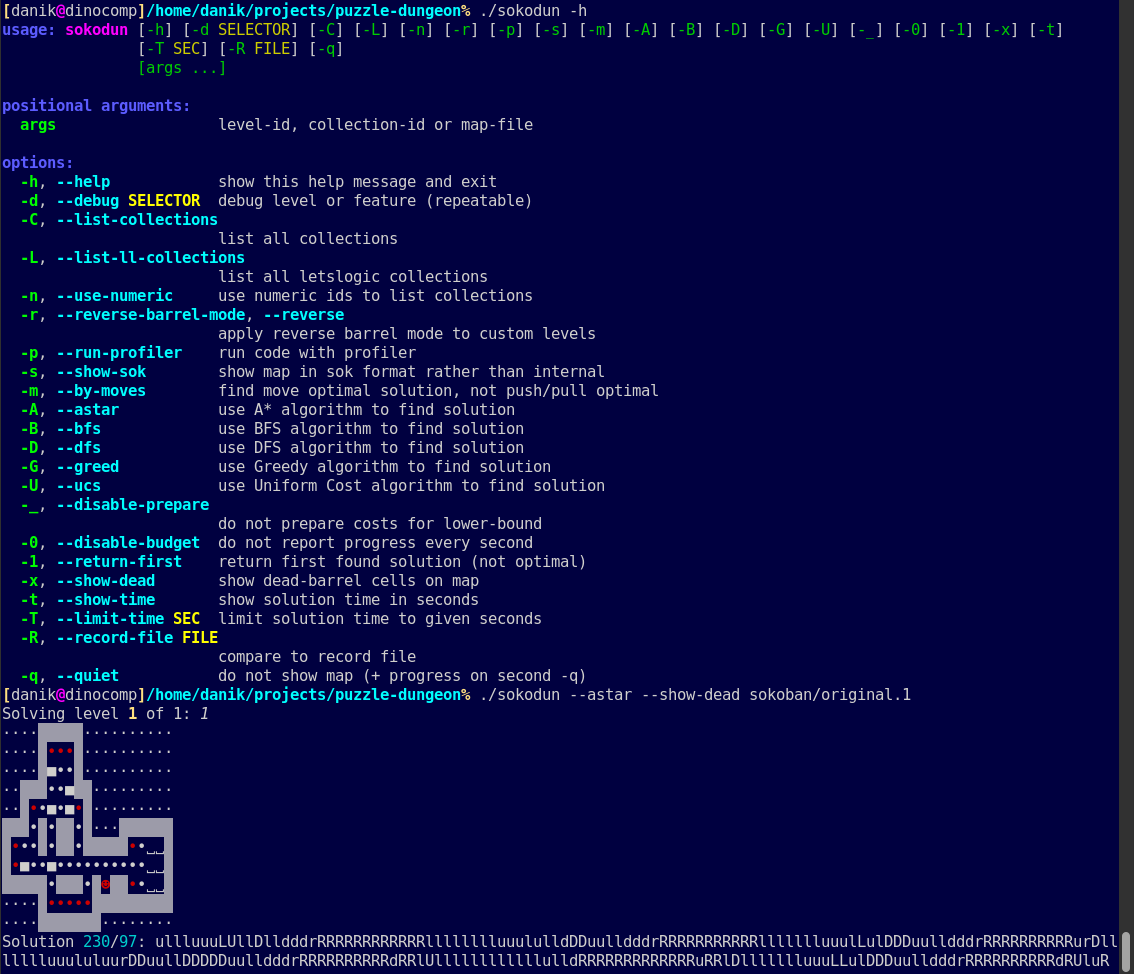
Run sokodun -h or sokodun --help from the
command line to see the full usage. The screenshot lists all options and
shows an example run. Your actual sokodun --help output may
be slightly different, since this is an evolving project.
Multiple levels or collections may be specified. Nearly all commonly used sources and formats of Sokoban maps are supported.
Level Selection
The following arguments may be used to construct a cumulative custom level collection:
- Collection IDs
→sokoban/takaken(only BarrelPuzzle collections are supported) - Level IDs
→sokoban/micro/picokosmos.3 - Map files (Sokoban map files and internal maps are
auto-detected)
→microcosmos.txt - Clipboard input (map or URL supported)
→clipboard: - Standard input (map or URL supported)
→stdin:or- - Map files via URL
→https://gamefaqs.gamespot.com/sg1000/916324-soukoban/faqs/50888 - LetsLogic collection IDs
→letslogic:30or"letslogic:Micro Cosmos" - LetsLogic level IDs (after loading their collection)
→letslogic:/2376
Multiple level ranges such as 2-10 or 15
are supported. They restrict the custom collection to the given level
numbers starting from 1.
Algorithm Selection
Exactly one algorithm may be selected:
-A,--astar
A* Search-B,--bfs
Breadth-First Search-U,--ucs
Uniform Cost Search-G,--greed
Greedy Search-D,--dfs
Depth-First Search
Solution Type
By default, the solver searches for push-optimal solutions. This may be changed as follows:
-m,--by-moves
Find move-optimal solutions instead of shift-optimal ones.
Solver Behavior
-1,--return-first
Return the first found solution (not necessarily optimal).-0,--disable-budget
Disable periodic progress reporting.-_,--disable-prepare
Disable heuristic preparation (debug use only).-T SEC,--limit-time SEC
Stop solving after the given time limit in seconds. Any solution found (even if non-optimal), or no solution, is returned.
Output Options
-s,--show-sok
Show the map in standard Sokoban format rather than the internal format.-x,--show-dead
Display dead-barrel cells. These are shown in red when color output is available, or as ☓ otherwise.-t,--show-time
Show solving time per level.-q,--quiet
Reduce output verbosity per level (repeatable, up to four-qflags).
Reverse Barrel Mode
-r,--reverse-barrel-mode
Enable pull-based solving for specified levels.
Records and Comparison
-R FILE,--record-file FILE
Compare results with stored records.
The record file is a text file containing one line per level. Each line contains either one m/p value or two space-separated m/p values, representing move-optimal and push-optimal records respectively.
By default, record comparison is performed automatically if the level metadata contains record information, such as:
- “Move-Record: m/p” and “Push-Record: m/p” headers following the map, or
- “Moves: m Pushes: p” header, which is treated as a move-optimal record.
Record comparison may be explicitly controlled:
- Always enable record comparison using -R .
- Always disable record comparison using -R “”
Progress Reporting
By default, sokodun prints periodic progress messages
during solving.
This can be disabled with --disable-budget.
Running on Windows
On Windows, run sokodun.bat wrapper. This is sometimes
preferable even in the bash environment.
The wrapper automatically detects a suitable Python installation
(using install-deps.bat --check-nogui) and runs the main
sokodun script using the detected interpreter. If no
suitable Python installation or required modules are found, the user is
prompted to run install-deps.bat to install Python and all
required dependencies.
Typing sokodun in cmd.exe or PowerShell
should invoke sokodun.bat. The usage and behavior should
match what is described here, except that Ctrl-C handling may
differ (Windows will first ask whether to terminate the batch job;
answer y).
In a bash environment, you may need to run ./sokodun.bat
to distinguish it from ./sokodun.
Examples
sokodun -A -t microcosmos.txt
sokodun -1 -q https://url-shortener.me/5NTJ 2-10
sokodun -1 -t -T 300 takaken.txt original-1-modified.txt letslogic:8 1-6 8-18
These commands solve the specified Sokoban collections or individual levels using the selected options (search algorithm, return-first mode, time limit, and output behavior).